¿Qué es la Industria IoT, o IIoT?
La Internet industrial de los objetos es el uso de dispositivos inteligentes conectados en aplicaciones industriales con fines como la automatización, la supervisión remota y el mantenimiento predictivo. El IIoT es una versión más robusta del Internet de las Cosas, o IoT, que es el reino de los dispositivos conectados en aplicaciones comerciales y de consumo.
En los casos de uso de Industrial IoT , los dispositivos inteligentes pueden desplegarse en vehículos de construcción, robótica de la cadena de suministro, energía solar y eólica, sistemas de sensores agrícolas, irrigación inteligente y mucho más. Estas aplicaciones IIoT tienden a tener algo en común: se despliegan en entornos difíciles y requieren los sensores y dispositivos más robustos.
Hay casos de uso de la IIoT en la industria ligera, como los contadores, y en la industria pesada, como las cintas transportadoras utilizadas en la minería, donde los dispositivos pueden estar sometidos a una amplia gama de factores ambientales, desde calor y frío extremos hasta humedad y vibraciones. Y en la Industria 4.0, procesos como la automatización de la fabricación y el mantenimiento predictivo requieren comunicaciones rápidas de máquina a máquina para la precisión y el control de robots, equipos y procesos.
La Internet Industrial de las Cosas consiste en desplegar sensores y máquinas inteligentes para capturar y mover datos, detectar cambios de temperatura, caudal o volumen, automatizar procedimientos en aras de la eficiencia, la precisión y la seguridad, entregar datos a las manos adecuadas para su análisis y toma de decisiones, y garantizar que todos esos procesos se produzcan a tiempo y de forma fiable y segura.
El poder del procesamiento Edge y la automatización en la industria IoT
El uso de dispositivos inteligentes se ha extendido rápidamente y, hoy en día, con el enorme crecimiento de IoT y la IIoT, es difícil encontrar una industria que no se vea afectada por este fenómeno. Hoy en día, las organizaciones industriales buscan trabajar de forma más inteligente, no más dura. Las redes rápidas, la computación de borde y la automatización pueden crear mejoras y eficiencias sin precedentes que simplemente no son posibles con una fuerza de trabajo humana. Esto no quiere decir que los humanos no sean necesarios. Al contrario, se necesitan ingenieros, desarrolladores de aplicaciones, científicos de datos y trabajadores de todo tipo para poner en marcha estas soluciones y hacer uso de ellas.
Obtenga nuestro resumen de soluciones
Descubra cómo la computación de borde resuelve los retos de las redes
Descargar PDF
Edge Computing para el procesamiento rápido de datos
La computación de borde procesa los datos en el extremo de la red, antes de transmitirlos a la nube, lo que aporta ventajas económicas y una respuesta en tiempo real. Al integrar el procesamiento de borde en el ecosistema industrial IoT , los gestores de red pueden aumentar drásticamente la eficiencia operativa. En las aplicaciones de la Industria 4.0, esta funcionalidad crítica, combinada con la velocidad y el rendimiento de la red 5G, permite la transferencia de datos en tiempo real necesaria para las aplicaciones que requieren más datos, como la automatización de la fabricación y la robótica.
Incluso en los procesos industriales tradicionales, la computación de borde cambia las reglas del juego, ya que permite obtener información en tiempo real sobre operaciones remotas, así como ventajas clave como el mantenimiento predictivo, que alerta a los técnicos cuando determinadas condiciones sugieren un fallo inminente. Esto garantiza que los equipos industriales puedan responder de forma proactiva, a menudo antes de que se produzca un fallo.
Automatización para mayor eficacia y seguridad
Hoy en día, los dispositivos remotos proporcionan capacidades de detección, conocimiento de datos y automatización que ponen en marcha procesos industriales y garantizan el funcionamiento normal de la maquinaria remota. La automatización ofrece un enorme abanico de ventajas.
Como ejemplo sencillo, pensemos en el trabajador agrícola que antes tenía que conducir de un rincón remoto de la finca a otro para asegurarse de que los sistemas de riego o los ventiladores contra las heladas estaban encendidos a la hora correcta. Hoy en día, ese trabajador puede comprobar los sistemas desde un ordenador portátil, asegurarse de que todo funciona correctamente y desplazarse sólo al lugar que realmente necesita servicio. Si un sistema de riego de pivote central se ha desviado, por ejemplo, el trabajador puede utilizar el GPS para identificar rápidamente su ubicación y asegurarse de que vuelve a la posición correcta. En otras palabras, el Internet Industrial de las Cosas trata de mejorar la eficiencia y la precisión al tiempo que reduce los costes.
El impacto de la IIoT en los trabajadores y los puestos de trabajo es que los hace más eficientes y mejora la productividad. También reduce el "trabajo ajetreado" y la probabilidad de errores en tareas como el registro de datos, de las que se encarga mejor un dispositivo inteligente. La detección automatizada y la recopilación de datos en lugares peligrosos y de difícil acceso reducen incluso el riesgo para la vida humana. Y hace que los datos correctos lleguen antes al lugar adecuado para su evaluación. Cuando un empleado puede recibir una alerta en su teléfono inteligente de que un depósito está bajo mínimos o de que un equipo necesita mantenimiento, aumentan las probabilidades de que los problemas se resuelvan pronto, antes de que sean más caros o catastróficos.
Ejemplos de casos de uso industrial IoT
Una de las mejores formas de conocer cómo las empresas comerciales e industriales utilizan IoT es a través de los numerosos ejemplos de aplicaciones IIoT. Vamos a dar una vuelta por algunas de ellas.
Automatización de la fabricación
Los casos de uso de la Industria 4.0, incluida la automatización de la fabricación o "fabricación inteligente", han sido durante mucho tiempo una visión de futuro que un día combinaría las redes más rápidas y los dispositivos de borde más inteligentes con cámaras, sensores, IA y aprendizaje automático, así como robótica avanzada, para automatizar los procesos en toda la cadena de fabricación, desde el montaje y la detección de anomalías hasta el embalaje y el envío. Estas visiones se están haciendo realidad hoy en día, con la mayor disponibilidad de redes 5G de alta velocidad, el despliegue de dispositivos informáticos de borde 5G y la maduración de tecnologías avanzadas como la IA. En la actualidad, todas estas innovaciones y avances se están uniendo para hacer realidad la visión de la Industria 4.0.
El siguiente diagrama muestra la fabricación inteligente en la práctica.
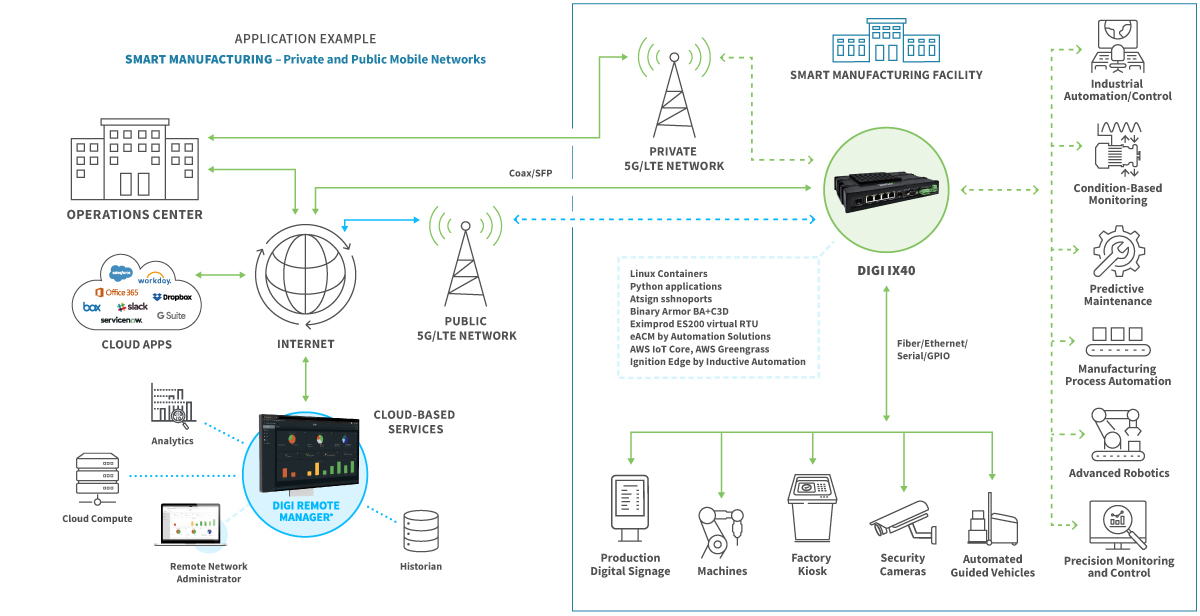
Mantenimiento Predictivo
Las aplicaciones de mantenimiento predictivo tratan de identificar cuándo un proceso empresarial crítico o un equipo corre el riesgo de averiarse, de modo que se pueda programar un mantenimiento proactivo y preventivo para solucionar los problemas con antelación y frustrar el tiempo de inactividad. Los métodos tradicionales pueden ser muy caros y los trabajadores pueden pasar por alto inadvertidamente indicadores de que el equipo está experimentando problemas. En muchos casos, los técnicos y trabajadores de mantenimiento han tenido que desplazarse tradicionalmente a lugares remotos para realizar comprobaciones manuales, sólo para tener que hacer otro viaje con una orden de trabajo, piezas de repuesto o baterías. Recibir una alerta de que se está produciendo un problema permite localizarlo y solucionarlo con un solo movimiento de la carretilla, a menudo antes de que el cliente final sea siquiera consciente del problema. El resultado es una mejora de las prácticas de mantenimiento, una reducción de los costes y una mayor satisfacción del cliente.
Estos son algunos ejemplos de aplicaciones de mantenimiento predictivo de la IIoT en distintos sectores.
- Supervisión de procesos - minería: En el clásico juego "Piedra, papel o tijera", la piedra puede ser vencida por el papel. Sin embargo, en el mundo real, la piedra le gana a todo. En las aplicaciones mineras, grandes cintas transportadoras trasladan tierra (montones de rocas) de una zona a otra a grandes distancias, más de un kilómetro en algunos casos, donde el material se procesa para extraer minerales valiosos. Si la cinta transportadora y el equipo de apoyo "se caen" o se paran, la mina puede perder millones de dólares en ingresos. Para garantizar que las cintas transportadoras funcionen sin interrupción, 24 horas al día, 7 días a la semana, se añaden sensores a la cinta transportadora para recopilar puntos de datos y enviarlos a través de un dispositivo de radio (por ejemplo, Digi XBee®) a una pasarela y, a continuación, a una aplicación de supervisión remota. Digi Remote Manager® puede ayudar a supervisar esas pasarelas y dispositivos en diferentes minas y canteras para evitar tiempos de inactividad no deseados.
- Mantenimiento de equipos - ascensores: La empresa de ascensores OTIS quiere asegurarse de que los clientes que instalan su producto reciben un servicio de la máxima calidad. En lugar de esperar a que surja un problema que afecte a las operaciones diarias y a la satisfacción del cliente, la empresa coloca sensores en cientos de miles de ascensores instalados. Estos sensores comunican puntos de datos a través de una pasarela a un entorno en la nube que proporciona información y notificaciones automatizadas a los técnicos de campo.
- Supervisión de activos - construcción: Una empresa de gestión energética ofrece soluciones a clientes como las constructoras. Desarrollan una gama de herramientas IoT para ayudar a estas organizaciones a asegurarse de que están optimizando el uso de los vehículos e identificando los problemas antes de que supongan una pérdida de ingresos. Para predecir el fallo de una manguera hidráulica antes de que provoque la avería del equipo, una costosa limpieza del fluido hidráulico y posibles lesiones, la empresa desarrolla una solución conectada que supervisa el equipo, identifica e informa sobre los puntos de datos que indican un posible fallo, y permite a los clientes establecer condiciones de alerta y recibir notificaciones automáticas.
Ejemplo de aplicación de mantenimiento predictivo
En el siguiente ejemplo, un módulo de radio Digi XBee® recopila datos de los equipos de un elevador de grano y los envía a un router industrial Digi IX40, que a su vez entrega esos datos a aplicaciones basadas en la nube para su visibilidad y posterior procesamiento. Si los datos indican ciertas condiciones, un técnico puede verlo en una aplicación en línea o recibir alertas de una aplicación como Digi Remote Manager®. El técnico puede trabajar en un proceso de solución de problemas de forma remota o enviar personal al lugar para realizar el mantenimiento necesario.
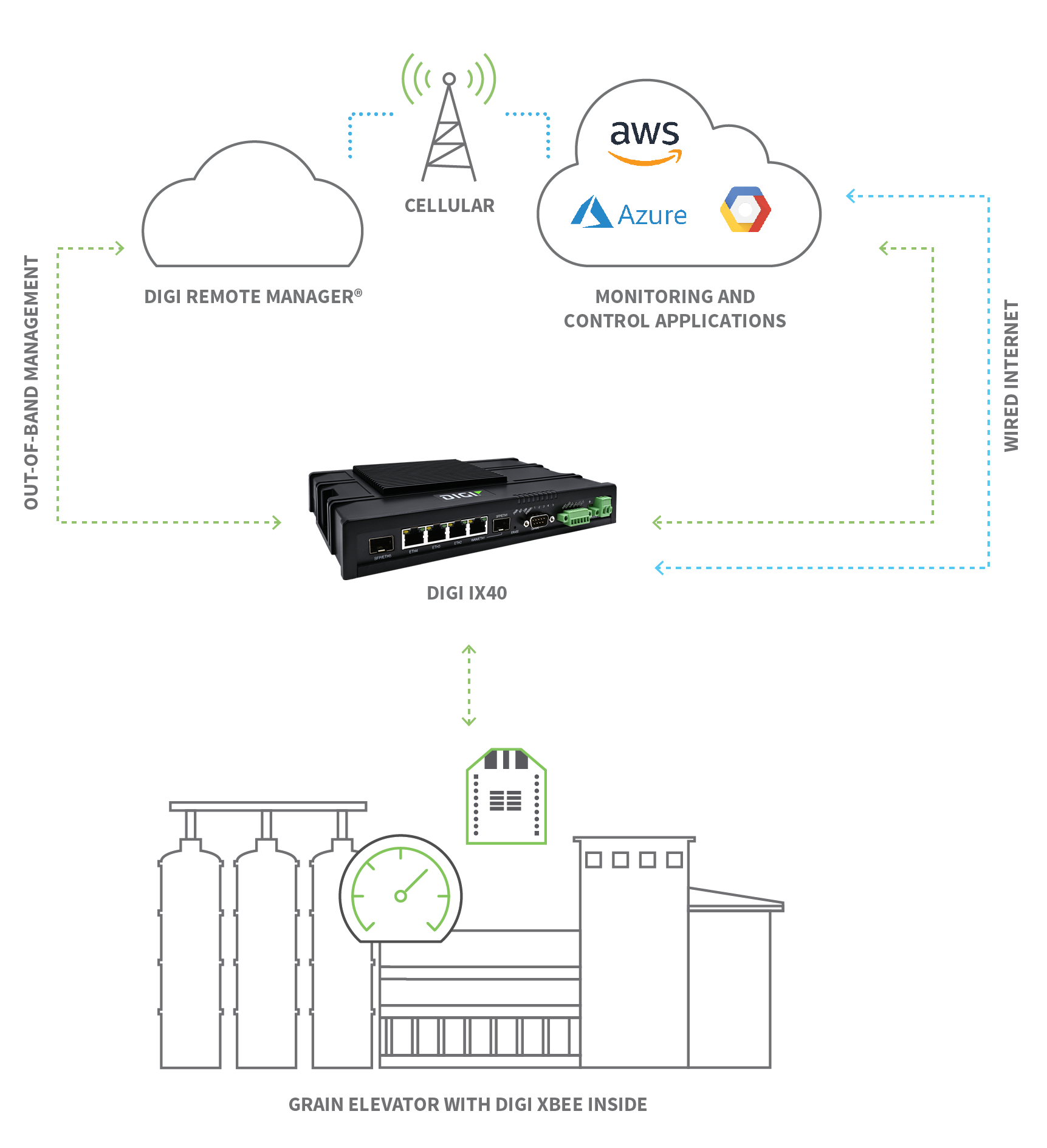
Control a distancia
La monitorización remota está en el centro de muchas aplicaciones industriales, porque tradicionalmente resulta ineficaz, caro y a menudo difícil o arriesgado vigilar lo que ocurre con los equipos sobre el terreno. Los equipos que requieren supervisión pueden estar situados en puestos avanzados remotos, en lo alto del alumbrado público, en el interior de un pozo o en las profundidades de una mina, por lo que no sólo resulta poco práctico supervisar manualmente ese activo, sino también caro y arriesgado.
Los siguientes son sólo algunos de los muchos ejemplos de supervisión remota en aplicaciones industriales.
- Monitorización de tanques - petróleo y gas: Tirar piedras a un tanque o usar un palo para golpear un tanque para determinar los niveles de fluido han sido prácticas comunes en el pasado que pueden mejorarse drásticamente con las aplicaciones de IIoT. Los tanques de los pozos petrolíferos de producción deben supervisarse para garantizar que no se produzcan desbordamientos, lo que puede acarrear cuantiosas multas y costes de limpieza. La supervisión de los tanques in situ con productos químicos que se inyectan en el fondo del pozo para reducir la corrosión de las tuberías también es una parte importante de las operaciones diarias. Para reducir el riesgo y optimizar la eficacia, una empresa puede instalar una solución automatizada de control de tanques que envíe lecturas de nivel según sea necesario (por minuto, hora o día) para que los responsables de campo puedan gestionar las recogidas o entregas, así como las llamadas de mantenimiento preventivo, basándose en datos reales y lecturas de nivel. Dar este paso también evita el coste de enviar personal a cada uno de los tanques en un programa de rotación, independientemente de los niveles del tanque. En su lugar, sólo envían personal cuando es necesario.
- Control del caudal - agricultura: Los pivotes centrales en agricultura son una forma habitual de distribuir el agua por los campos de cultivo. El agua pasa por una tubería y se distribuye a través de aspersores mientras el pivote central se mueve lentamente en círculo. Una fuga en un pivote central o en cualquier otra línea de riego puede causar daños importantes y costar miles de dólares en reparaciones y pérdida de recursos. La monitorización remota de la presión y el movimiento puede ayudar a identificar proactivamente problemas en una tubería de riego. Los cabezales obstruidos, las fugas o incluso los accesorios desconectados pueden detectarse con antelación y enviar alarmas para ayudar a los agricultores a evitar problemas, mantener el crecimiento de los cultivos y limitar el capital invertido en reparar problemas.
- Supervisión de procesos químicos - refinerías: La gestión remota no tiene por qué estar a 160 kilómetros. En muchos casos, puede estar a sólo 30 metros, o a un campo de fútbol. La supervisión en las instalaciones de procesamiento se ha hecho tradicionalmente con instalaciones de cables. Uno de los retos es que los cables son caros de instalar y mantener. Otro reto es que los sistemas cableados pueden estar sujetos a entornos corrosivos y otros factores como terremotos y fenómenos meteorológicos catastróficos. Una planta de procesamiento puede tener cientos o miles de sensores instalados para recopilar datos, por ejemplo para supervisar un lote de productos químicos, asegurarse de que está bajo control y evitar vertidos o explosiones. Hoy en día, empresas como estas recurren al Internet Industrial de las Cosas para supervisar y automatizar aún más los procesos, por ejemplo tomando lecturas y registrándolas en un sistema basado en la nube para análisis, informes y alertas a las que se puede acceder desde dispositivos móviles.
Control inalámbrico de depósitos con 1844myfuels
"Digi se ha convertido en parte de toda nuestra solución. Es el primero que es verdaderamente inalámbrico, ocupa poco espacio y funciona."
Leer el artículo
Ejemplo de aplicación de monitorización remota
En este ejemplo de monitorización remota, un módulo de radio recoge datos de un tanque industrial y los dirige a través de un procesador integrado a aplicaciones basadas en la nube para su monitorización, alertas y ajustes.
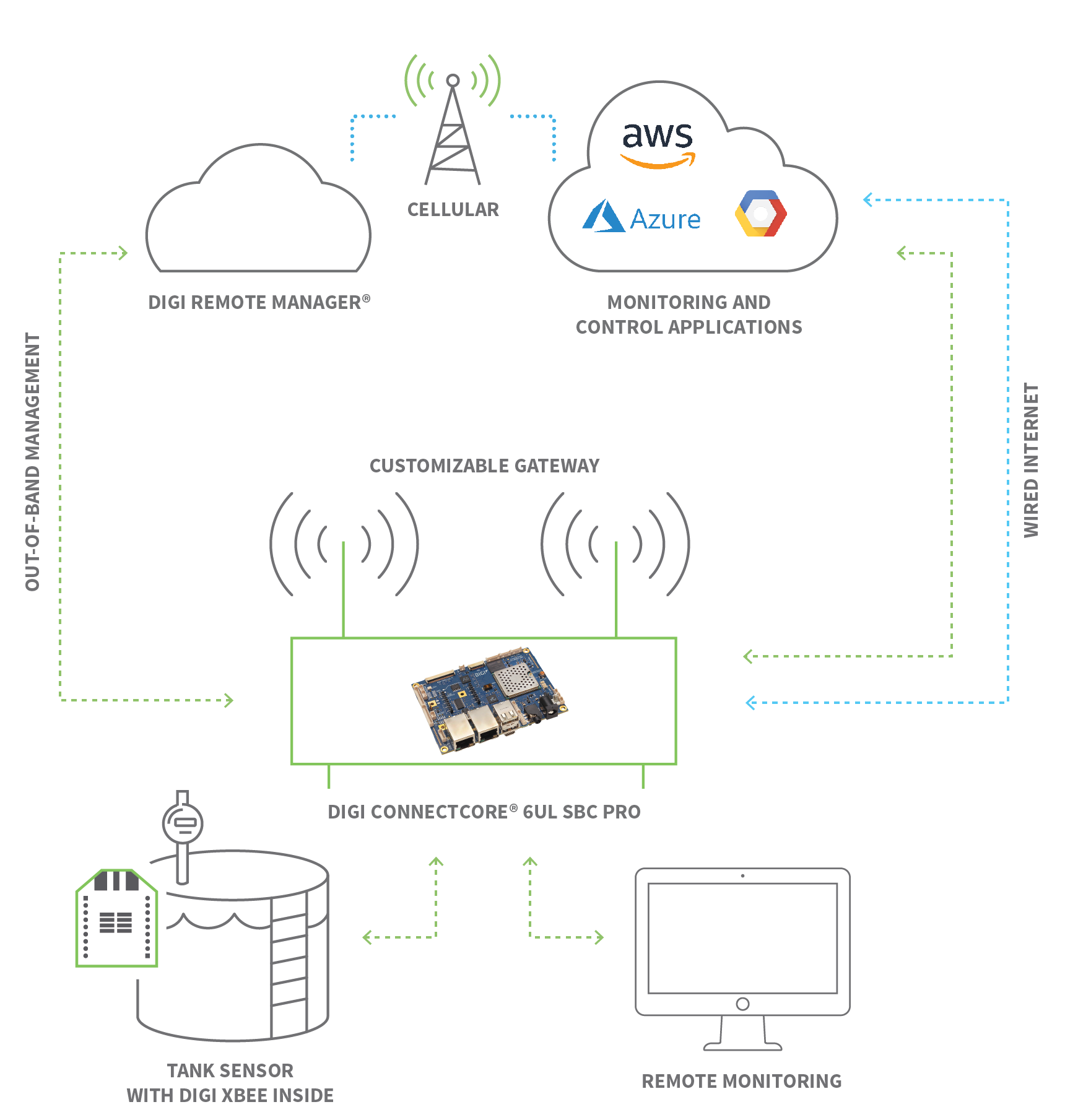
Automatización de procesos
La automatización de procesos que, de otro modo, requerirían la intervención humana, el desplazamiento de camiones o un trabajo manual ineficiente es otra de las razones más comunes para desplegar aplicaciones conectadas en el espacio industrial. La gama de casos de uso es muy amplia, pero las razones para poner en marcha estos procesos del Internet Industrial de las Cosas se reducen de nuevo a unos pocos factores clave: eficiencia, reducción de costes y reducción de riesgos.
Estos son algunos ejemplos de automatización en la IIoT.
- Riego inteligente - Los viejos tiempos en que se regaba de forma programada sólo porque se disponía de agua se están evaporando poco a poco (valga el juego de palabras). Hoy en día, los agricultores están adoptando la tecnología para supervisar las condiciones del suelo y el clima, entre otros factores, para determinar cuándo y dónde se necesita agua. Los sensores de humedad del suelo conectados a módulos inalámbricos que transmiten los datos de los sensores a pasarelas y luego a la nube permiten a los agricultores controlar las condiciones de cultivo. Y la automatización del proceso de riego en función de las lecturas de humedad garantiza el uso eficiente de los recursos hídricos: dónde, cuándo y durante cuánto tiempo es necesario regar.
- Modificación automática - El sector de la energía apuesta hoy por la automatización para modificar el comportamiento de los equipos en función de las condiciones. Por ejemplo, el viento suele enfriar las cosas en un caluroso día de verano. Pero demasiado viento puede causar estragos en todo tipo de entornos, como la agricultura, los molinos de viento y las instalaciones solares. Cuando se levantan vientos fuertes en un campo solar, las estaciones meteorológicas pueden controlar cuándo la velocidad del viento puede alcanzar umbrales perjudiciales. La comunicación inalámbrica desde una pasarela puede enviar órdenes a los paneles solares para que se muevan a una posición de seguridad que ayude a reducir o evitar daños en estos activos de alto coste.
- Fanáticos de las heladas - No hay nada como una helada temprana para arruinar la cosecha de fin de año. Del mismo modo, una helada tardía en primavera puede dañar las plantas que están a punto de florecer. La tecnología de sensores inalámbricos combinada con ventiladores gigantes en cultivos de alto valor en huertos y viñedos permite a los agricultores controlar las condiciones meteorológicas para poder encender los ventiladores y limitar los daños de las heladas tempranas o tardías. Es un poco como tener un sistema de calefacción y aire acondicionado para los cultivos. Sin embargo, estos ventiladores deben encenderse manualmente cuando se producen heladas inesperadas. Esto significa que los agricultores deben hacer la ronda a cada uno de los puntos en los que han instalado ventiladores alrededor de sus acres, a menudo en mitad de la noche. Una aplicación que automatice estos procesos no sólo puede detectar cuándo las temperaturas se acercan al rango de las heladas, sino también activar un proceso para poner en marcha los ventiladores. Mientras tanto, el agricultor puede descansar tranquilo por la noche y ver de un vistazo desde un dispositivo móvil qué ventiladores se han encendido y si funcionan correctamente.
Ejemplo de aplicación de automatización de procesos
En el siguiente ejemplo de automatización de procesos, los sensores de suelo recogen datos, que son enrutados por un módulo Digi XBee con MicroPython a una pasarela industrial Digi XBee , y luego a aplicaciones de supervisión y control remoto basadas en la nube. Una de estas aplicaciones lanza automáticamente los procesos, mientras que otra permite a los gestores o administradores de la red asegurarse de que todos los dispositivos y procesos funcionan como se espera.lanza
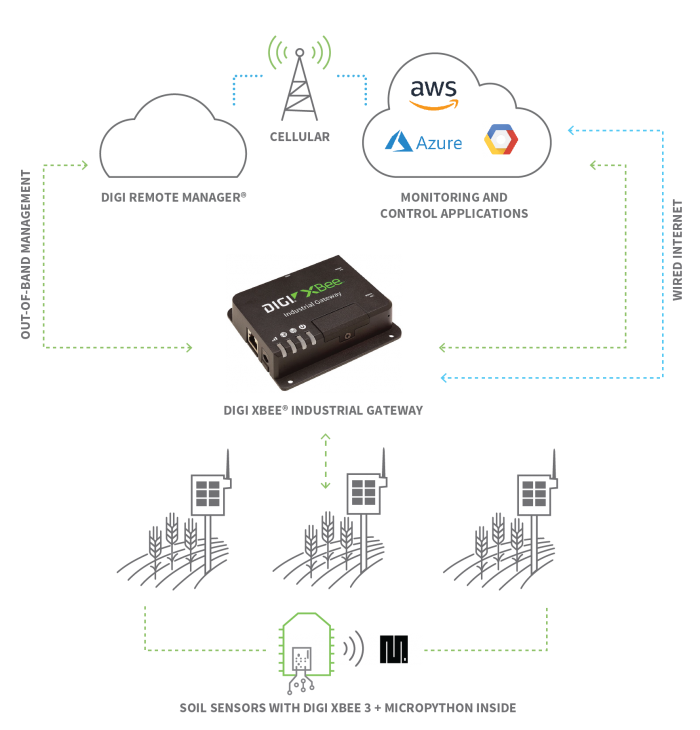
Consideraciones importantes para las aplicaciones industriales IoT
Hay muchas cosas que hay que tener en cuenta a la hora de evaluar los dispositivos y la configuración adecuados para su aplicación industrial IoT . Entre ellas se encuentran las cuestiones relativas a la distancia a la que sus dispositivos IIoT necesitarán transmitir datos, así como la frecuencia de envío de los mismos, si la tecnología de radiofrecuencia o celular es la adecuada para su aplicación, y muchas otras decisiones que repercuten en la planificación general, la implantación, la escalabilidad y la gestión de su proyecto y que, en última instancia, afectan a su coste total de propiedad.
Cubriremos algunas de las cosas que hay que tener en cuenta mientras se prepara para diseñar, construir y desplegar su proyecto. Si tiene preguntas o está listo para evaluar soluciones, los miembros del equipo de Digi pueden asociarse con usted para realizar una evaluación completa de sus necesidades de aplicación. Y los equipos de diseño e ingeniería de Digi también están disponibles para cualquier nivel de apoyo en el desarrollo de su aplicación IIoT. Póngase en contacto con nosotros para iniciar esa conversación.
Dispositivos industriales frente a herramientas de creación de prototipos:
Un paso fundamental para las aplicaciones industriales de IoT -y, de hecho, para cualquier producto profesional que se enfrente a retos ambientales como temperaturas fluctuantes o vibraciones- es encontrar el producto adecuado para el trabajo. Si desarrolla un producto para una aplicación como, por ejemplo, un servicio de uso compartido de bicicletas en la ciudad, puede que técnicamente no se considere una aplicación industrial, pero sus requisitos son similares, ya que tendrá que ser capaz de soportar movimientos bruscos, cambios de temperatura y humedad. Algunos tipos de dispositivos pueden soportar factores ambientales difíciles, y otros son menos adecuados. Por eso es fundamental evaluar la robustez de un producto y si está diseñado para la aplicación prevista.
Hay muchos módulos de bajo coste que son excelentes para la creación rápida de prototipos y para proyectos de estudiantes, como Raspberry Pi y Arduino. Su atractivo coste es una buena razón para utilizar estos productos en fases iniciales. Pero querrá un producto con calificación industrial diseñado para la viabilidad a largo plazo en entornos exigentes cuando busque productos que sean adecuados para aplicaciones IIoT.
Algunos de los factores a evaluar en un producto incluyen:
- Control de calidad de la fabricación
- Disponibilidad y estabilidad del producto a largo plazo
- Rangos de temperatura probados
- Flexibilidad de diseño y programabilidad
- Disponibilidad de herramientas de apoyo y bibliotecas de código
- Capacidad para actualizar el firmware de forma proactiva, sobre todo cuando su despliegue se amplía más allá de unos pocos dispositivos
- Certificaciones en las regiones donde se desplegará su aplicación.
Empezar con una herramienta de creación de prototipos es una buena manera de probar un concepto; pero cuando esté listo para ir al campo con dispositivos desplegados, asegúrese de seleccionar dispositivos con clasificación industrial.
Estrategia de gestión a distancia
Los métodos de mantenimiento tradicionales, que consisten en enviar un camión al campo para supervisar o gestionar los equipos, se vuelven rápidamente poco prácticos y costosos cuando hay que mantener docenas, cientos o incluso miles de dispositivos. Al igual que su teléfono móvil, que tiene actualizaciones de firmware que se envían regularmente, los dispositivos tienen actualizaciones de firmware y parches de seguridad que deben enviarse a cada uno de los dispositivos de su red IIoT para mantener esos dispositivos actualizados y seguros. Una solución de gestión remota le permite enviar correcciones de errores y mejoras de funciones a todos sus dispositivos sobre el terreno, independientemente del tamaño de su red.
Para implantar una estrategia de gestión remota, busque una solución que le permita realizar actualizaciones remotas de firmware, conectividad de dispositivos y diagnósticos remotos desde cualquier lugar, utilizando un dispositivo inteligente. Por ejemplo, Digi Remote Manager es una solución basada en la nube que proporciona estas capacidades y más, permitiéndole establecer alertas para una serie de condiciones, descargar archivos y supervisar automáticamente las configuraciones de los dispositivos y restablecerlas a la versión correcta en caso de manipulación.
Poner en marcha un sistema de gestión remota es muy económico en comparación con el coste de enviar un camión para actualizar manualmente el firmware de un dispositivo montado en una señal o una farola, y permite a su gestor de red controlar todos los dispositivos, independientemente de cuántos tenga en su red o de dónde estén en el mundo.
Conclusión:
La evaluación y la toma de decisiones que conllevan el desarrollo y la implementación de una aplicación IIoT pueden ser desalentadoras. Digi puede ayudarle a identificar la solución adecuada para sus necesidades en cualquier punto del camino, desde el alcance inicial del proyecto hasta los servicios completos de ingeniería y certificación.
Tanto si desea demostrar el retorno de la inversión de un nuevo producto como si necesita cumplir un plazo estricto de conformidad o por presiones del mercado, Digi puede asociarse con usted para lograr esos objetivos. El tiempo de comercialización puede ser especialmente crítico cuando existe una ventana de oportunidad de corta duración para adelantarse a la competencia.
Trabajar con una empresa que ha demostrado su profesionalidad en consultoría e ingeniería no sólo le da la seguridad de que podrá cumplir los plazos y fechas de lanzamiento, sino que también le ayuda a completar las revisiones de diseño y obtener asistencia para la certificación cuando sus recursos no dan más de sí.
Próximos pasos